
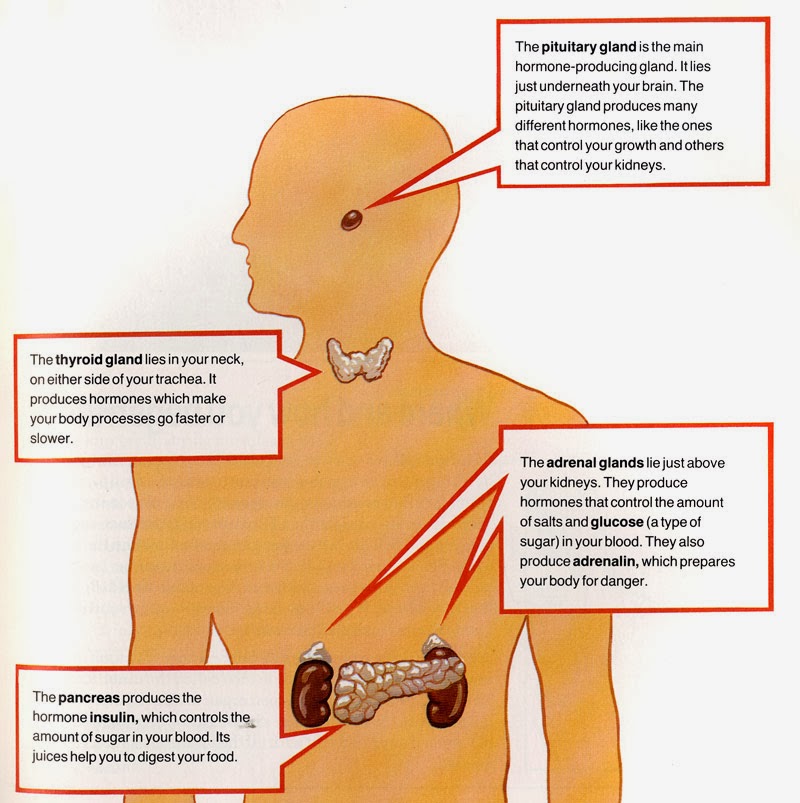
What is cushing's syndrome/hypercortisolism? Has 3 forms: adrenal tumours secrete cortisol independent of ACTH, non-pituitary ACTH or CRH secreting tumours, excess pituitary production of ACTH. Treatment is life-long aldosterone and cortisol replacement therapy. Also with cortisol deficiency causes weakness, fatigue and hypoglycaemia. Which area of the adrenal gland secretes aldosterone? Zona glomerulosa What is addisons disease? Deficiency of aldosterone secretion, causing Na wastage and K retention, dehydration, circulatory collapse and death. How does aldosterone maintain blood pressure? It is dedicated to conversing Na, and if you conserve sodium in body fluid you maintain blood pressure. What is the K wasting affect? Exchange of intra-tubular Na with extracellular K. What is the principle role of aldosterone? To maintain high Na:K in the plasma by promoting Na reabsorption and K secretion in the distal tubule of the nephron. What stimulates aldosterone to be produced? Structure in kidney sensitive to SNS, blood pressure and Na:K ratio in blood, so if blood pressure/Na:K ratio falls or SNS stimulated it will secrete renin to activate the chain of events. Renin stimulates angiotensin 1, which stimulates angiotensin 2 in the lungs, which stimulates aldosterone. What regulates aldosterone production? Renal regulation of secretion via renin/angiotensin. Increase CHO storage and synthesis but decrease its utilisation which can lead to hyperglycaemia, Lipolytic actions, Inhibits inflammatory process and reduces immune response. Required for normal hepatic glucose formation. What stimulates an ACTH rise? Stress What is the function of cortisol? Mobilises AA from skeletal muscle, stimulate AA uptake from liver and induction of hepatic enzymes for GNG. If there was no cortisol ACTH and CRH would remain high. What inhibits cortisol? It has a negative feedback system where it inhibits its own production by acting at the anterior pituitary and hypothalmus. ACTH travels around the body i the jugular vein. What stimulates glucocorticoids (cortisol)? ACTH (adrenocorticotrophic hormone), which is dependent on CRH (corticotrophin releasing hormone). androgens What is the function of the sex steroids? They are considered unimportant because the amount produced by the adrenal gland is small. What does the cortex secrete? Mineralocorticoids eg. adrenaline What is the medulla? A sympathetic nervous system ganglion which secretes adrenaline and sometimes noradrenaline into the bloodstream rather than innervating post-ganglionic fibres What is the neurotransmitter that activates the medulla? Noradrenaline What is the function of catecholamines? Back up for sympathetic nervous system, fight/flight, importantly it increases availability of glucose and stimulates K uptake by cells to maintain ECF.

Zona reticularis Inner most region, a tangle of cells What does the medulla secrete? Catecholamines eg.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
